Can You Get a Virus From a Not Secure Website?

We all know websites aren’t created equal when it comes to security. But can you get a virus from a not secure website?
Indeed, can visiting or clicking links expose you to malware and other threats?
Let’s explore what ‘non-secure’ really means and how to stay safe even in the shady corners of the internet. Ready?
Can I get a virus from clicking a not secure website?
Yes, you can get a virus from clicking a not secure website. That’s because it doesn’t use the encryption protocol HTTPS to secure the communication between your browser and its server. Instead, it uses an outdated unencrypted HTTP connection.
That makes your data vulnerable to interception and manipulation. Clicking the pages and links within such a site can certainly infect your system.
However, it also means malicious actors can potentially access any information you send or receive. This includes personal data, login credentials, and financial information.
What are the potential threats?
Let’s have a closer look at the biggest threats you might face from a not secure website.
Man-in-the-middle attacks
HTTP-only sites are susceptible to man-in-the-middle attacks.
In short:
Malicious actors can intercept the communication between your browser and the website. They can then view and modify the transmitted data. So, not only will they gain unauthorized access to your data but they may also manipulate it.
Additionally, cybercriminals may steal your login credentials and credit card details if you enter them into unsecured fields.
Malware and viruses
Attackers have a higher success rate of injecting malicious code into unsecured websites.
Visitors may then unknowingly download malware onto their devices and compromise their system and data. Typically, this happens via drive-by download attacks.
The victims accidentally download malicious files by clicking on a link or pop-up. Drive-by attacks can be:
- Authorized — when users intentionally download software but don’t know it’s harmful
- Unauthorized — when users unintentionally get malware onto their device.
Phishing attempts
Not-secure websites can also be used to carry out phishing attacks. During these scams, hackers try to trick you into entering your personal information, like login credentials or credit card numbers.
They also often replace legitimate pages on a compromised site with fake ones to steal this data.
Similarly, phishing sites spread through spam emails and phone messages are usually hosted in a non-secure environment without HTTPS.
Let’s say you open a link to Amazon but it uses HTTP. In that case, it’s probably a phishing duplicate.
Note: It’s important to understand the lack of security doesn’t automatically mean the website is malicious.
But it does mean the information exchanged between you and the website isn’t protected. And that’s risky!
How to stay safe on sites without an SSL certificate?
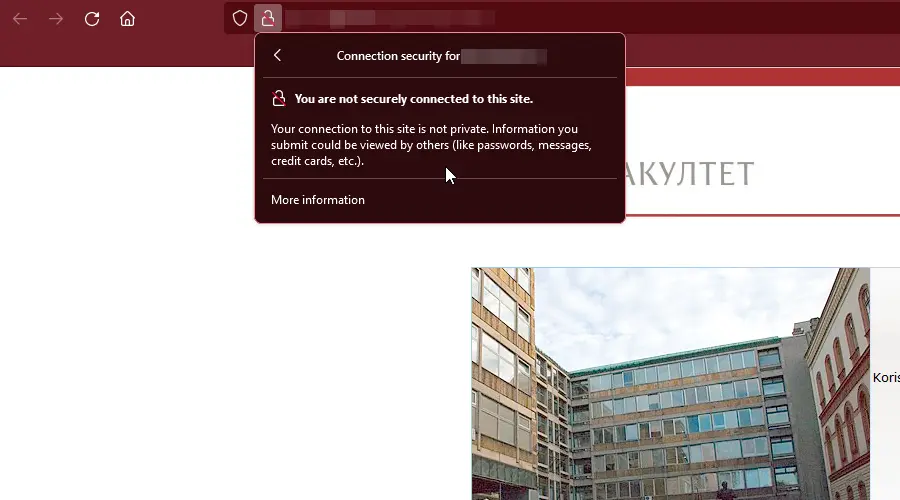
To identify whether a website is secure or not, look for a padlock in the browser’s address bar.
A closed padlock or ‘https://’ at the beginning of the URL indicates a secure connection. The Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate is present.

On the other hand, an open padlock or ‘http://’marks a non-secure connection with no SSL certificate.
Here are some tips for staying safe online:
- Only enter personal information on secure websites with the padlock and HTTPS.
- Don’t download anything from a non-secure website unless you have strong real-time antivirus protection.
- Be wary of any emails or messages with links that start with HTTP.
- Use a browser with HTTPS-only settings, such as the Brave browser.
- Get an extension to encrypt your communication with websites, like HTTPS Everywhere.
- Consider extra protection such as a firewall (different from an antivirus) or a VPN to encrypt all your internet traffic.
If in doubt, remember to use a reliable antivirus or internet security software on your device. It can help detect and block potential threats. Keep this software updated to stay protected against the latest threats.
Summary
So, can you get a virus from a not secure website? Yes, though this is only one of the risks when visiting a website without an SSL certificate. Any data you send could be intercepted. You’re also at higher risk of phishing attempts.
Luckily, staying alert and heeding our security recommendations will help you avoid danger. Good luck!



User forum
0 messages