9 Keypoints to Compare Cloud Vs On-Premise Security

As the new threats are evolving every day, data security is becoming a major challenge for organizations. Choosing the right platform to protect sensitive data is a crucial decision. Cloud Vs On-Premise security, which one is better?
This is a detailed article that covers almost everything about Cloud and On-Premise Servers and their security levels.
If you want to read the comparison between Cloud and On-Premise security, jump to the final part of the article.
And for in-depth information, keep reading till the end.
In short
Cloud Servers are equally secure, flexible, less costly, highly scalable, user-friendly, and require fewer resources and time as compared to On-Premise Servers. The only drawback of cloud servers is less Control over data as compared to On-Premise Servers.
Cloud Vs On-Premise Security: Short Summary
- Key Points about Cloud Vs On-premise Security
- Cloud Servers are now equally secure to On-premise Servers.
- For more security the data can be encrypted in all the states (at rest, in motion, and in use) in cloud servers.
- In cloud computing the client has less control over data as compared to On-premise servers.
- Cloud computing is preferred over On-premise servers because of shared responsibility of security which reduces the workload of organizations.
- Cloud computing involves only software monitoring while in case of On-premise both hardware and software monitoring takes place.
- In case of cloud computing identifying and fixing the issues is easy but in case of On-premise, it is very complicated and requires expertise.
What is Cloud Server/ Cloud Computing?

The Cloud Servers are the stack of multiple Datacenters located at different locations.
Cloud computing is the name of the cloud server’s technology. This technology is responsible for the fastest delivery of data to the user’s end.
The word cloud is used because the data from any corner of the world is hosted from the multiple locations of the data centers.
This data can also be accessed from any corner of the world by the user.
What Cloud Computing can Deliver?
- Self service Provisioning and On-demand computing
- Pooling of Resources
- Rapid Elasticity and highly scalable
- Only Pay for what you use
- Measured Services
- Resiliency and Availability
- Improved Security
- Access of Broad Network
Types of Cloud Servers
- Public Servers
- Private Servers
- Hybrid Servers
Public Servers
Public data servers are not restricted to high data security. The data hosted on such servers are available publically.
Anyone can access this data without any security hindrance.
For example, Websites and Apps are hosted on public cloud servers.
Private Servers
Private data servers are used to host extremely confidential and sensitive data. The data available on these servers are not publically available.
Data stored on private servers are highly secured, encrypted, and can’t be accessed by unauthorized users.
For Example, the Data of Security Agencies and financials of organizations is hosted on Private cloud servers.
Hybrid Servers
This is the most popular type of cloud data hosting server among Organizations. Hybrid cloud servers have common characteristics of both Public and Private servers.
Hybrid servers provide both public and private cloud space for storage.
Organizations can host their business websites on a public server and store sensitive data on private cloud storage.
Delivery Models of Cloud Computing
The services offered by Cloud Computing are based on three delivery models. Cloud computing works on the shared responsibility model, as we have discussed earlier.
The shared responsibilities changes according to these delivery models. The consumer can choose the delivery model depending on how much responsibility he wants to take on.
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
This service model provides Infrastructure as a service.
The organizations that don’t want to build and maintain their own infrastructure of storage, use this service.
IaaS provides servers, computing resources, networking, and storage as a service. There is no need to purchase any hardware.
It requires some software to access, configure, and establish an uninterrupted connection between the organization and server.
This model of cloud computing is also scalable as per requirement.
The client takes on maximum responsibility as he has complete control over the server space.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service)
Platform as a Service model provides the platform having resources like servers, computing resources, networking, storage, and development suit.
An organization that not only wants to store the data but also tests develops and hosts the apps.
They can use this model of service efficiently.
The responsibility of the service provider is to handle the security, operating systems, and backups.
PaaS service model requires some specific software to access the service.
This model of service is also scalable.
- SaaS (Software as a Service)
This is an all-in-one model which provides servers, computing resources, networking, storage, development suit, and software.
The best part of this model is, it doesn’t require any kind of software at the client’s end.
The client can access the services just through an API provided by the service provider.
This is the most preferred cloud computing service model because of ease of access.
SaaS model doesn’t require any hardware or software at the client’s end.
There is no need to install, upgrade and manage any kind of software.
It is a highly scalable cloud computing service model also.
Because the storage space is completely managed by the service provider, the shared responsibility of the client is very limited.
Cloud Vs On-Premise Security: What is On-Premise Server

This is the traditional way of storage and hosting.
This is an in-house data center that is architecture, programmed, installed, managed, and monitored by the dedicated in-house team.
The hardware, software, policies, regulations, and licenses are upgraded and installed by the team of the organization.
On-premise servers provide complete control over data but are highly expensive.
These servers require more dedicated resources but downtime is extremely low.
Many large and medium organizations are still using On-premise data servers because of data security reasons.
Cloud Vs On-Premise Security: What is Cloud Security?
Giant organizations like LinkedIn, Apple, and Sony experienced cyber-attacks in the past.
These cyber-attacks were succeeded because of some loopholes in the security system.
Cloud security is a critical factor for an organization.
So, what is cloud security?
“Cloud Security refers to the implementation of the latest and innovative technologies and techniques to prevent the data security breach in the cloud servers.
Cloud security also covers the architecture, development, and installations of a stack of servers.
Finding out the loopholes in security and regularly updating software is also the part of Cloud security.”
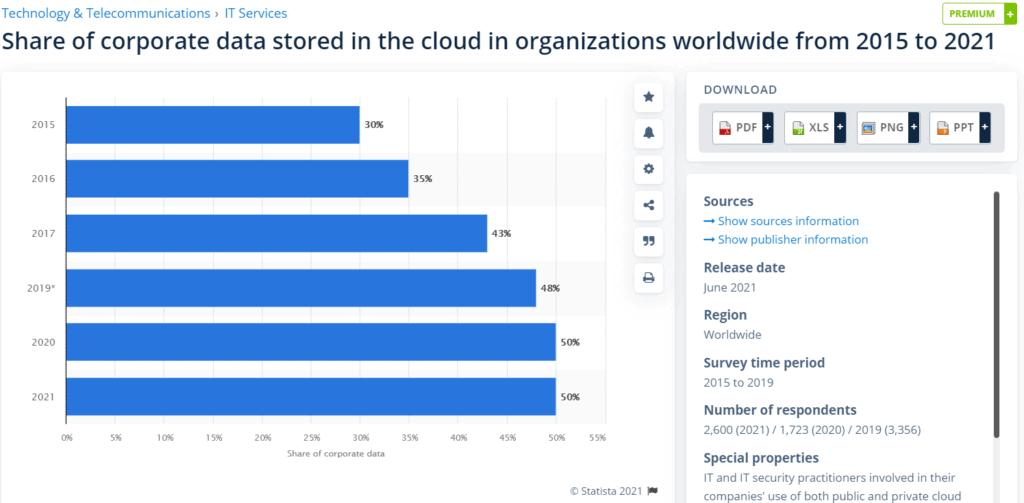
The below graph shows the share of corporate data moved to Cloud Servers since 2015.
Elements of Cloud Security
There are many key elements are involved in the Architecture, development, and installation of cloud security.
These elements can represent the whole picture of the process and help you understand easily.
- Cloud Service Provider (CSP)
The company that provides you the Cloud service like AWS (Amazon Web Services), Google Cloud, Azure, etc.
Cloud Service Providers are responsible for the Security, Maintenance, and sufficient Storage availability.
The cloud server system is based on the Shared responsibility of CSP and Customer.
- CWPPs (Cloud Workload Protection Platforms)
CWPP is a tool provided by CSPs to consistently protect the workload of an application or data.
This tool helps to manage the sudden increase in traffic or data and protects the application against crashes.
- CASBs (Cloud Access Security Brokers)
This tool is also provided by Cloud Service Providers. The basic responsibility of this tool is to serve as a Gatekeeper between customer data and cloud service.
CASB is responsible to check and verify the data that is being uploaded by the user.
- CSPM (Cloud Security Posture Management)
Cloud Security Posture Management is a group of products or services.
The key responsibility of CSPM is to monitor the security and compliance issues in the cloud server.
CSPM is a crucial tool provided by Cloud service providers.
- SASE (Secure Access Service Edge)
SASE is a model of Cloud Security.
Secure Access Service Edge is the Organization of Network and Security tools in one management console.
This model provides a user-friendly interface to customize the setting to protect and secure the data.
- ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access)
ZTNA is a Cloud Security Model which is responsible to grant or deny access to a particular network or device.
Zero Trust Access network basically assumes every network and device as insecure and untrusted before providing access.
The role of ZTNA is very critical in cloud server security.
What is On-premise Security?
Many sophisticated organizations like security agencies still prefer an On-premise approach to data storage.
Fundamentally this approach provides them more control over data and its security.
Knowing the fact that this method requires giant money and permanent expert resources to maintain the whole ecosystem.
Cloud Vs On-premise Security: Comparison
The points mentioned below will clear all your confusion about the security level difference between Cloud and On-premise servers.
I also have mentioned the points to ensure maximum security.
Cloud Security
- As we know cloud computing works on shared responsibility model, security is the responsibility of cloud service provider (CSP).
- There must not be any vulnerability in the Application because it can create data security challenges.
- The cloud platform offers encryption of data to protect the confidential and sensitive data. You can “Bring Your Own Key (BYOK)” or “Keep Your Own Key (KYOK)” for more control over data.
- The built-in security at every step is the beauty of cloud computing.
- It is easy to manage access of users and networks and setup compliance and security accordingly.
- Shared Responsibility of cloud network reduces the workload of an organization which helps them to concentrate their work.
- Cloud Network is now equally secure as On-premise infrastructure but more flexible than On-premise infrastructure.
- It is easy to monitor, audit, and fixing the problems.
- For highly confidential and sensitive data the encryption takes place at every step whether it is at rest, in-motion or in-use.
On-premise Security
- Highly expert and dedicated team is required to monitor the security and fix the issues.
- Owner has complete control over data that means he is responsible for security and issues.
- Highly expensive tools are needed to monitor, maintain and fix the issues.
- Many organizations rely on On-premise approach to store and host their business because of complete control over infrastructure, security and data.
- The biggest problem with this approach is it requires huge money, highly expert resources, considerable time, and space. This is not a cost effective approach.
- The security level of On-premise approach is very high.
- It is not easy to monitor, audit and fix the issues as the system is very complex.
- On-premise approach involves the security of both software and hardware.
Cloud Vs On-premise Security: Best Practices
- In the process of developing an application the security must be forethought not afterthought.
- Scan and fix the vulnerabilities in application before deploying it for public.
- Do not open up your application data for the whole world. Use Firewalls and filters to prevent unauthorized access.
- Encryption of data should be applied to the data at rest and in motion.
- To increase the security level use two factor authentication.
- For high data security deploy firewalls, Intrusion Prevention security measures, and antimalware.
- Take regular backups of your cloud data and isolate it from cloud space.
- Take audit log on regular basis and monitor it.
Cloud Vs On-premise Security: Final Words
An organization can’t afford a data security compromise. Now we have discussed a lot about Cloud Vs On-premise security.
This article is highly informative and will help you to decide to select the one that fulfills your requirement.
Cloud servers are now equally secure and client-oriented just like the On-premise method.
Many organizations are now moving their data to cloud platforms because of affordability, flexibility, scalability, high-security features.
What do you think about this topic? Write in the comment section.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Is cloud more secure than On-premise?
Nowadays cloud computing is equally secure but more flexible, scalable, and affordable than On-premise servers.
- Is On-premise More Secure?
In terms of security, On-premise is preferred over Cloud computing. But nowadays both of them are equally secure.
- On-Premise Vs Cloud Pros and Cons
Cloud computing is highly flexible, scalable, and affordable. It doesn’t require a high upfront cost and can be used on pay per use basis.
Whereas On-premise requires a high upfront cost and is less scalable, flexible, and affordable as compared to cloud computing.
- On-Premise Meaning
The meaning of On-Premise is “Hands-on Security”.
- Is IaaS a Cloud?
IaaS stands for “Infrastructure as a Service”. This is one of the three models of Services of Cloud Computing.
The Other Models are PaaS (Platform as a Service) and SaaS (Software as a Service).
- Is Azure Stack a Private Cloud?
Azure is Microsoft’s Cloud Service Provider (CSP) which is a Private Cloud Network.
- Why Public Cloud is not Secure?
Public Cloud is an open-source platform that can be accessed by anyone. The internal security of the public cloud is not so strong and can be breached by advanced hacking methods.



User forum
0 messages